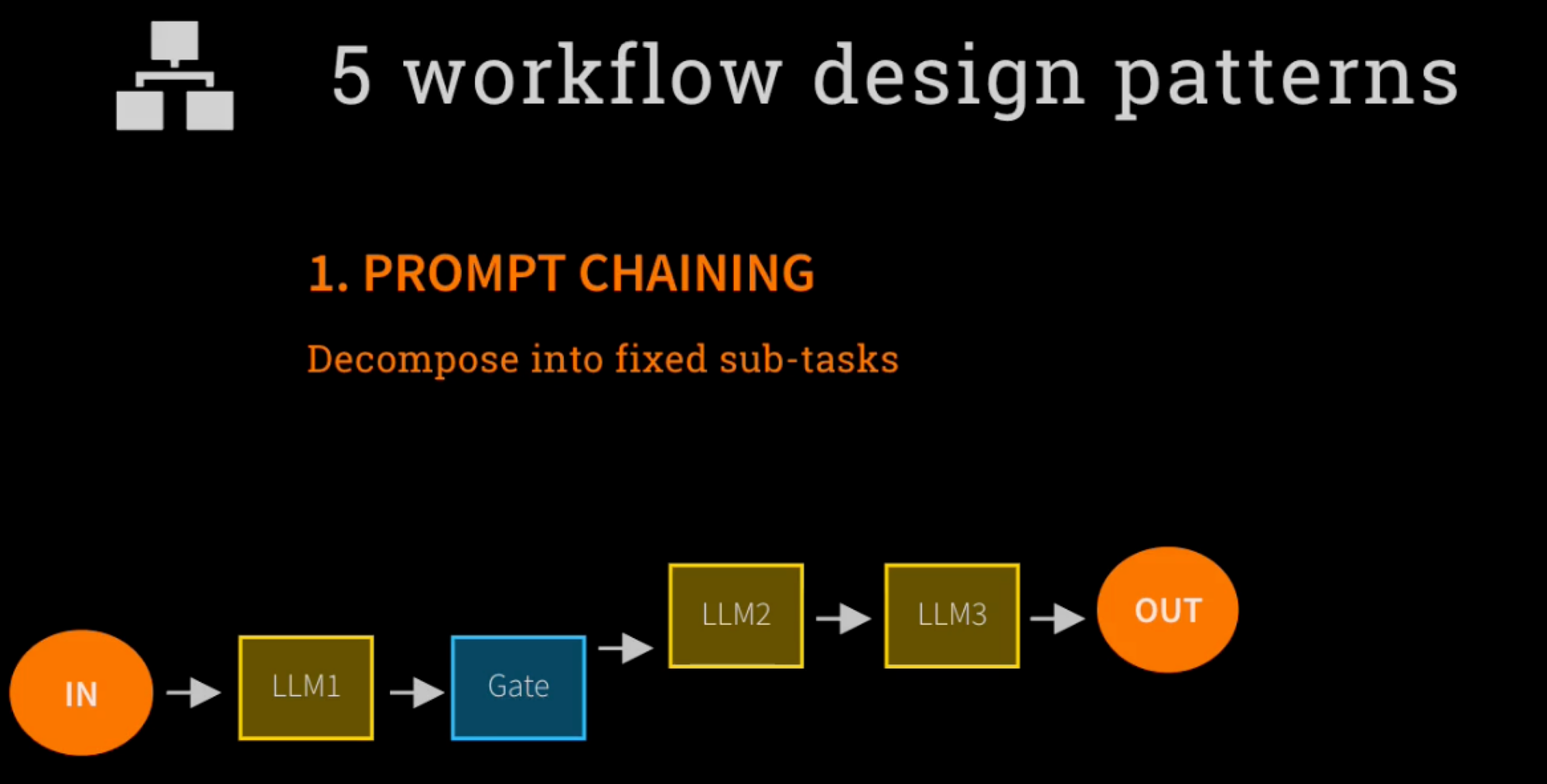
Prompt Chaining
Definition
Prompt chaining is a natural language processing (NLP) technique, which leverages large language models (LLMs) that involves generating a desired output by following a series of prompts. In this process, a sequence of prompts is provided to an NLP model, guiding it to produce the desired response. The model learns to understand the context and relationships between the prompts, enabling it to generate coherent, consistent, and contextually rich text.
Advantages
Prompt chaining offers several advantages over traditional methods used in prompt engineering. By guiding the model through a series of prompts, prompt chaining enhances coherence and consistency in the text generation leading to more accurate and engaging outputs.
Consistency
By requiring the model to follow a series of prompts, prompt chaining helps maintain consistency in the text generation. This is particularly important in applications where maintaining a consistent tone, style, or format is crucial, such as in customer support or editorial roles [5].
In customer support, prompt chaining can be used to ensure consistent communication with users. For example, the bot might be prompted to address the user using their preferred name or follow a specific tone of voice throughout the conversation.
Enhanced control
Prompt chaining provides greater control over the text generation, allowing users to specify the desired output with precision. This is especially useful in situations where the input data is noisy or ambiguous, as the model can be prompted to clarify or refine the input before generating a response[6].
In a text summarization system, prompt chaining allows users to control the level of detail and specificity in the generated summary. For instance, the user might first be prompted to provide the content that they're interested in summarizing, such as a research paper. A subsequent prompt could follow to format that summary in a specific format or template.
Reduced Error Rate
Prompt chaining helps reduce error rates by providing the model with better context and more focused input. A structured prompt chaining is helpful to reduce the human efforts and validate the code and outputs more faster. By breaking down the input into smaller, manageable prompts, the model can better understand the user's intentions and generate more accurate and relevant responses[7].
In a machine translation system, before translating a sentence, the system might first prompt the user to specify the source language, target language, and any relevant context or terminology. This helps the model to better understand the source text and generate an accurate translation.
Questions for Self-Assessment
- What is the fundamental difference between a single, complex prompt and a prompt chain? How does this difference address the limitations of traditional prompt engineering?
- The text suggests that prompt chaining improves consistency and reduces error rates. Based on the examples provided (customer support, machine translation), how does the structured, step-by-step nature of a prompt chain contribute to these advantages?
- Beyond the use cases mentioned, can you think of a new application where breaking a complex task into a prompt chain would be more effective than a single prompt? Why would this be the case?
- How might the "build a reference library" step for prompt chains relate to the concept of reusable code in software engineering? What are the benefits of this approach for developers and customer service representatives?
Fundamental Differences & Advantages
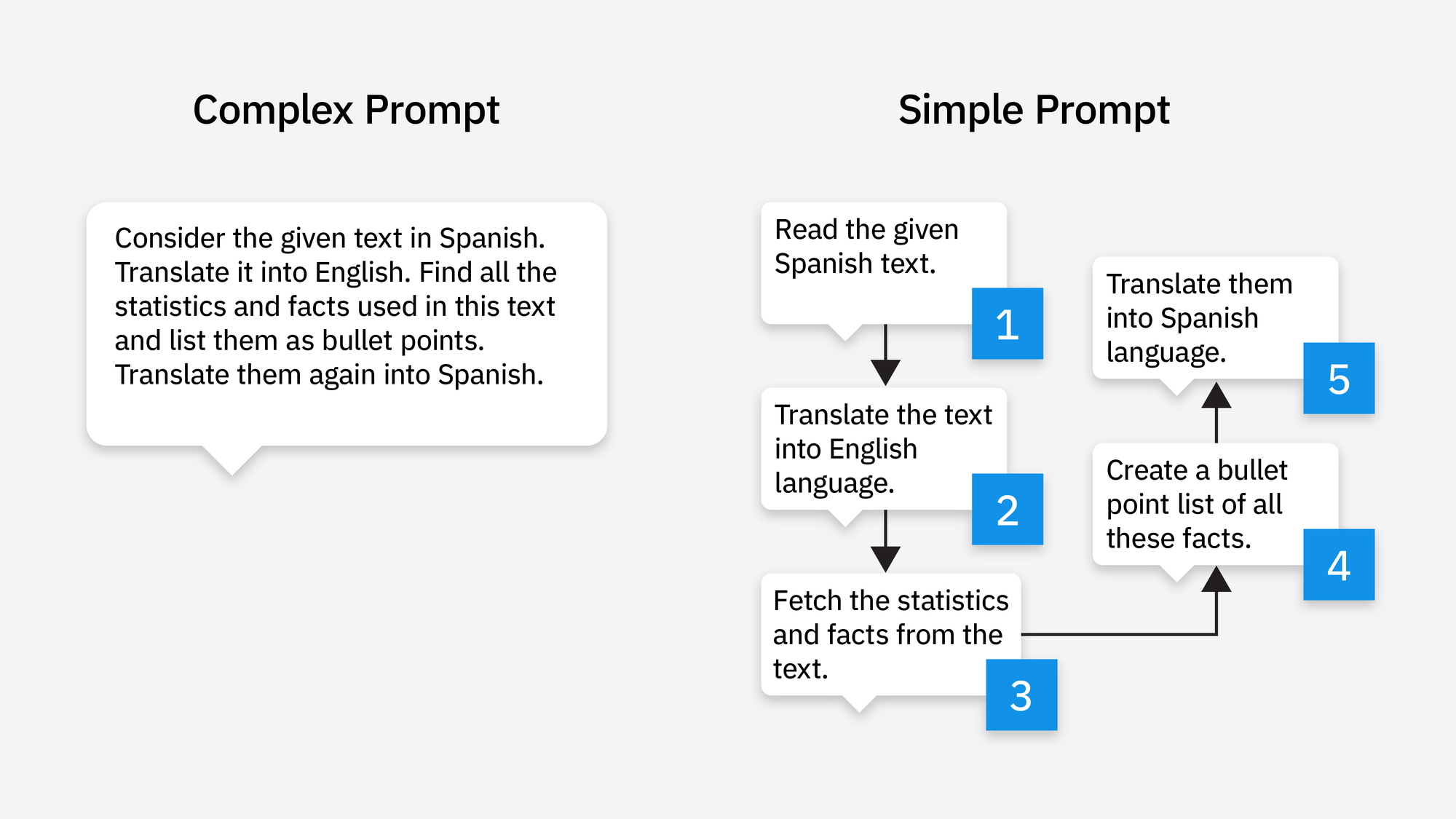
The fundamental difference between a single, complex prompt and a prompt chain lies in their approach to task execution. A single, complex prompt attempts to solve a multi-step problem with one monolithic instruction, which can overwhelm the model and lead to errors or a lack of clarity. In contrast, a prompt chain breaks down the same complex task into a sequence of simpler, more manageable prompts, where the output of one step serves as the input for the next. This difference addresses the limitations of traditional prompt engineering by providing the model with a clear, guided path, reducing ambiguity and improving the overall quality and reliability of the output.
Improved Consistency & Reduced Errors
The structured, step-by-step nature of a prompt chain directly contributes to improved consistency and reduced error rates by controlling the flow and context of information. For instance, in customer support, a prompt chain can ensure a consistent interaction by first prompting the model to identify the user's name, then to check their account status, and finally to provide a tailored response. This prevents the model from attempting all actions at once and potentially missing a critical step or using an inconsistent tone. Similarly, in machine translation, the chain first prompts the model to identify the source language, then to translate the text, and finally to format the output. This sequential process ensures each step is completed correctly before moving to the next, significantly lowering the chance of translation errors.
New Application of Prompt Chaining
A new application for prompt chaining could be legal document summarization and analysis. A single, complex prompt asking a model to "summarize this 50-page legal contract and identify all clauses related to intellectual property and liability" would likely lead to a generalized or incomplete response.
A prompt chain, however, would be more effective:
- Prompt 1: "Identify and list all sections and sub-sections within the document."
- Prompt 2: "From the list, extract the full text of all sections containing keywords like 'patent,' 'copyright,' 'trademark,' or 'liability.'"
- Prompt 3: "Summarize the key points of each extracted section, highlighting the obligations and rights of each party."
This structured approach ensures that no critical section is missed, and the final output is precise and accurate, making the complex task of legal analysis more efficient and reliable.
Reference Library as Reusable Code
The concept of building a "reference library" of prompt templates for prompt chaining is directly analogous to using reusable code libraries or functions in software engineering.
- For Developers: Just as a developer uses a pre-written function to perform a common task (e.g., sorting an array) instead of writing the code from scratch, a prompt engineer can use a pre-built prompt template for a common task (e.g., summarizing a document, extracting data). This saves significant time and effort, ensures consistency, and reduces the likelihood of introducing errors.
- For Customer Service Representatives: This approach allows for the creation of standardized, effective conversation flows. A representative could simply select a template like "Issue Resolution Chain" or "Product Inquiry Chain" to guide an AI assistant. This ensures that every customer interaction follows a proven, successful path, leading to better user experiences and more efficient problem-solving. It transforms a complex, creative task into a systematic, repeatable process.
